World’s fastest XML Tutorial
- XML son las siglas de eXtensible Markup Language.
- XML fue diseñado para almacenar y transportar datos.
- XML fue diseñado para ser legible tanto por humanos como por máquinas.
Hoy aprenderemos los conceptos basicos de XML porque muchos sistemas usan esta tecnologia y debemos al final horientarlos a las posibles vulnerabilidades que se pueden presentar en sistemas que tengan XML.
Tenemos el siguiente codigo:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<bookstore>
<book category="cooking">
<title lang="en">Everyday Italian</title>
<author>Giada De Laurentiis</author>
<year>2005</year>
<price>30.00</price>
</book>
<book category="children">
<title lang="en">Harry Potter</title>
<author>J K. Rowling</author>
<year>2005</year>
<price>29.99</price>
</book>
<book category="web">
<title lang="en">Learning XML</title>
<author>Erik T. Ray</author>
<year>2003</year>
<price>39.95</price>
</book>
</bookstore>
Con su arbol XML de la siguiente manera:
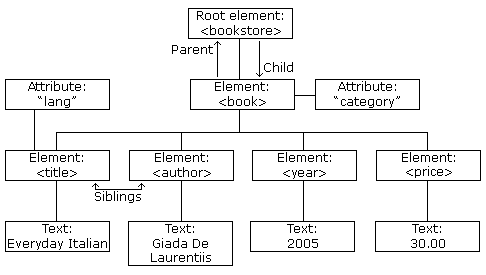
¿Qué es un elemento XML?
Un elemento XML es todo, desde (incluida) la etiqueta inicial del elemento hasta (incluida) la etiqueta final del elemento.
<price>29.99</price>
Un elemento puede contener:
- texto
- atributos
- otros elementos
- o una mezcla de los anteriores
Elementos XML vacíos
<element></element>
También puede utilizar una etiqueta de cierre automático:
<element />
- Los elementos vacíos pueden tener atributos.
Reglas de nombres XML
Los elementos XML deben seguir estas reglas de nomenclatura:
- Los nombres de los elementos distinguen entre mayúsculas y minúsculas
- Los nombres de los elementos deben comenzar con una letra o un guión bajo
- Los nombres de los elementos no pueden comenzar con las letras xml (o XML, o Xml, etc.)
- Los nombres de los elementos pueden contener letras, dígitos, guiones, guiones bajos y puntos.
- Los nombres de los elementos no pueden contener espacios
XML Attributes Must be Quoted
<gangster name='George "Shotgun" Ziegler'>
<gangster name="George "Shotgun" Ziegler">
XML Namespaces
Creamos XML Namespaces, para no tener conflicto a la hora de unir documentos XML, ya que pueden contener elementos con el mismo nombre pero que expresan algo diferente.
<root>
<h:table xmlns:h="http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/">
<h:tr>
<h:td>Apples</h:td>
<h:td>Bananas</h:td>
</h:tr>
</h:table>
<f:table xmlns:f="https://www.w3schools.com/furniture">
<f:name>African Coffee Table</f:name>
<f:width>80</f:width>
<f:length>120</f:length>
</f:table>
</root>
La declaración de espacio de nombres tiene la siguiente sintaxis. xmlns:prefix=”URI”.
Tambien se puede especificar en la raiz del documento
<root xmlns:h="http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/" xmlns:f="https://www.w3schools.com/furniture">
Tambien se puede expresar como un atributo para que no se tenga que expresar en cada uno de los elementos.
<table xmlns="http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/">
<tr>
<td>Apples</td>
<td>Bananas</td>
</tr>
</table>
<table xmlns="https://www.w3schools.com/furniture">
<name>African Coffee Table</name>
<width>80</width>
<length>120</length>
</table>
XMLHttpRequest
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h2>Using the XMLHttpRequest Object</h2>
<div id="demo">
<button type="button" onclick="loadXMLDoc()">Change Content</button>
</div>
<script>
function loadXMLDoc() {
var xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhttp.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (this.readyState == 4 && this.status == 200) {
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML =
this.responseText;
}
};
xhttp.open("GET", "xmlhttp_info.txt", true);
xhttp.send();
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
XML Parser
<html>
<body>
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
var text, parser, xmlDoc;
text = "<bookstore><book>" +
"<title>Everyday Italian</title>" +
"<author>Giada De Laurentiis</author>" +
"<year>2005</year>" +
"</book></bookstore>";
parser = new DOMParser();
xmlDoc = parser.parseFromString(text,"text/xml");
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML =
xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("title")[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue;
</script>
</body>
</html>
DOM XML
"El Modelo de Objetos de Documento (DOM) del W3C es una plataforma e interfaz de lenguaje neutro que permite a los programas y scripts acceder y actualizar dinámicamente el contenido, la estructura y el estilo de un documento."
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
var parser, xmlDoc;
var text = "<bookstore><book>" +
"<title>Everyday Italian</title>" +
"<author>Giada De Laurentiis</author>" +
"<year>2005</year>" +
"</book></bookstore>";
parser = new DOMParser();
xmlDoc = parser.parseFromString(text,"text/xml");
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML =
xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("title")[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue;
</script>
</body>
</html>
XPath
- XPath es un elemento importante en el estándar XSLT.
-
XPath se puede utilizar para navegar a través de elementos y atributos en un documento XML.
- XPath es una sintaxis para definir partes de un documento XML
- XPath usa expresiones de ruta para navegar en documentos XML
- XPath contiene una biblioteca de funciones estándar
- XPath es un elemento importante en XSLT y en XQuery
- XPath es una recomendación del W3C
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<bookstore>
<book category="cooking">
<title lang="en">Everyday Italian</title>
<author>Giada De Laurentiis</author>
<year>2005</year>
<price>30.00</price>
</book>
<book category="children">
<title lang="en">Harry Potter</title>
<author>J K. Rowling</author>
<year>2005</year>
<price>29.99</price>
</book>
<book category="web">
<title lang="en">XQuery Kick Start</title>
<author>James McGovern</author>
<author>Per Bothner</author>
<author>Kurt Cagle</author>
<author>James Linn</author>
<author>Vaidyanathan Nagarajan</author>
<year>2003</year>
<price>49.99</price>
</book>
<book category="web">
<title lang="en">Learning XML</title>
<author>Erik T. Ray</author>
<year>2003</year>
<price>39.95</price>
</book>
</bookstore>
XPath Expression Result
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/bookstore/book[1] Selects the first book element that is
the child of the bookstore element
/bookstore/book[last()] Selects the last book element that is
the child of the bookstore element
/bookstore/book[last()-1] Selects the last but one book element
that is the child of the bookstore element
/bookstore/book[position()<3] Selects the first two book elements that
are children of the bookstore element
//title[@lang] Selects all the title elements that have
an attribute named lang
//title[@lang='en'] Selects all the title elements that have
a "lang" attribute with a value of "en"
/bookstore/book[price>35.00] Selects all the book elements of the bookstore
element that have a price element with a value
greater than 35.00
/bookstore/book[price>35.00]/title Selects all the title elements of the book
elements of the bookstore element that have
a price element with a value greater than 35.00
XSLT
simplexsl.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<?xml-stylesheet type="text/xsl" href="simple.xsl" ?>
<breakfast_menu>
<food>
<name>Belgian Waffles</name>
<price>$5.95</price>
<description>Two of our famous Belgian Waffles with plenty of real maple syrup</description>
<calories>650</calories>
</food>
<food>
<name>Strawberry Belgian Waffles</name>
<price>$7.95</price>
<description>Light Belgian waffles covered with strawberries and whipped cream</description>
<calories>900</calories>
</food>
<food>
<name>Berry-Berry Belgian Waffles</name>
<price>$8.95</price>
<description>Light Belgian waffles covered with an assortment of fresh berries and whipped cream</description>
<calories>900</calories>
</food>
<food>
<name>French Toast</name>
<price>$4.50</price>
<description>Thick slices made from our homemade sourdough bread</description>
<calories>600</calories>
</food>
<food>
<name>Homestyle Breakfast</name>
<price>$6.95</price>
<description>Two eggs, bacon or sausage, toast, and our ever-popular hash browns</description>
<calories>950</calories>
</food>
</breakfast_menu>
simple.xsl
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<html xsl:version="1.0" xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform">
<body style="font-family:Arial;font-size:12pt;background-color:#EEEEEE">
<xsl:for-each select="breakfast_menu/food">
<div style="background-color:teal;color:white;padding:4px">
<span style="font-weight:bold"><xsl:value-of select="name"/> - </span>
<xsl:value-of select="price"/>
</div>
<div style="margin-left:20px;margin-bottom:1em;font-size:10pt">
<p>
<xsl:value-of select="description"/>
<span style="font-style:italic"> (<xsl:value-of select="calories"/> calories per serving)</span>
</p>
</div>
</xsl:for-each>
</body>
</html>
Referencias
- https://www.w3schools.com/xml/default.asp